Does it happen with you that you learned about all the array methods at the beginning of your Web Dev learning journey? Then you only remember a handful of them. The ones that are often used like map(), filter(), forEach().
And you end up doing something like:
function checkAllDateFormatsForPalindrome(date) {
const dateArray = getAllDateFormats(date);
const palindromes = dateArray.filter((date) => isPalindrome(date));
return palindromes.length;
}
// usage of the function checkAllDateFormatsForPalindrome
if (checkAllDateFormatsForPallindrome(date)) {
output.innerHTML = `Yay! Your birthday is a palindrome 🚀`;
}
// rest of the code
Here, I was checking if the dateArray contains a date that qualifies as a Palindrome using a filter function. Then returning the length of the const palindromes which will return length. However, I don't need the length, I only needed a bool value.
So, instead of using filter() we can directly use some() method. And it will return a bool value. The some() method checks if at least one element passes the test condition in the provided calling function.
So, the checkAllDateFormatsForPalindrome() function looks like this now:
//refactored checkAllDateFormatsForPalindrome() function
function checkAllDateFormatsForPalindrome(date) {
const dateArray = getAllDateFormats(date);
return dateArray.some((date) => isPalindrome(date));
}
So, writing this blog so that I come back again and again to find an array method that will be helpful for a situation like the above.
map
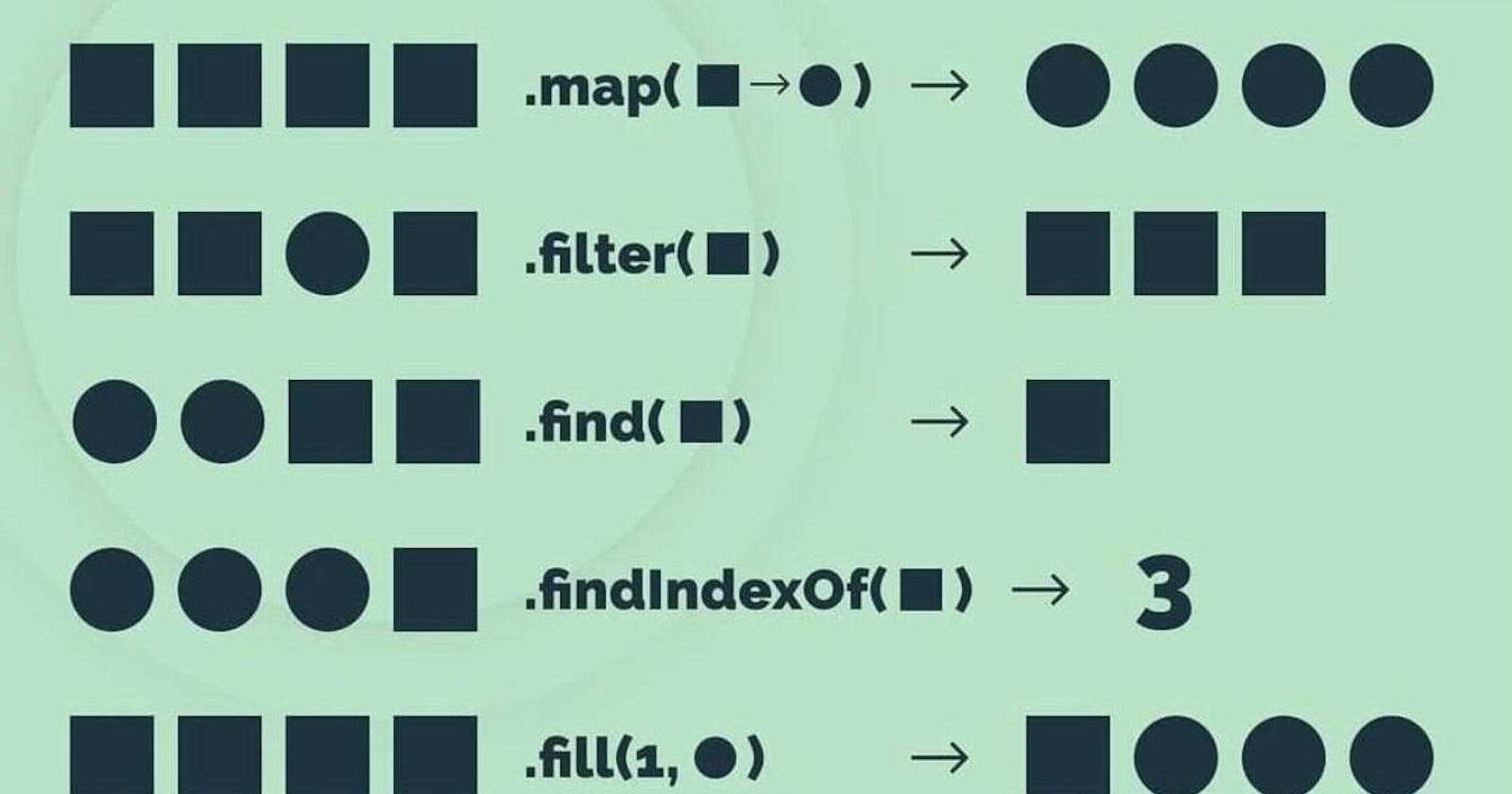
The map method creates a new array by iterating through the elements and calling a provided function on every element.
const arrayOfNumbers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10];
const mappedArray = arrayOfNumbers.map(num=> num/ 2);
console.log(mappedArray) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
filter
The filter method creates a new array with the elements that pass a given condition in the calling function.
const arrayOfNumbers = [3, 4, 5, 8, 12, 15];
const filteredArray = arrayOfNumbers.filter((num) => num% 2 === 0);
console.log(filteredArray); // [4, 8, 12]
reduce
The reduce method calls a defined reducer function for each element and returns a single value.
const arrayOfNumbers = [3, 4, 5, 8, 2, 15];
const reducedValue = arrayOfNumbers.reduce((total, current) => total + current);
console.log(reducedValue); // 37
find
The find method returns the first element that passes the given condition in the calling function
const arrayOfNumbers = [3, 4, 5, 8, 2, 15];
const numberFound = arrayOfNumbers.find((num) => num > 4);
console.log(numberFound); // 5
findIndex
The findIndex method is very similar to the find method, except it returns the index of the first element that passes the given condition in the calling function
const arrayOfNames = [
"Chanakya",
"Maharana Pratap",
"Shershaah",
"Charak",
"Sangram",
];
const indexOfName = arrayOfNames.findIndex((item) => item === "Shershaah");
console.log(indexOfName); // 2
forEach
The forEach method iterates through all the elements of an array and calls a provided function for each element.
const arrayOfNames = [
"Chanakya",
"Maharana Pratap",
"Shershaah",
"Charak",
"Sangram",
];
arrayOfNames.forEach((item) => console.log(item));
// Chanakya
// Maharana Pratap
// Shershaah
// Charak
// Sangram
The difference between map() & forEach() is that, the former returns a new array and the latter returns undefined.
every
Theevery()method checks if all elements pass the test condition in the provided calling function. It also returns a boolean value.
const arrayOfNames = [
"Chanakya",
"Maharana Pratap",
"Shershaah",
"Charak",
"Sangram",
];
const doesContainName = arrayOfNames.every((item) => item === "Shershaah");
console.log(doesContainName); // false
some
Thesome()method checks if at least one element passes the test condition in the provided calling function. It returns a boolean value. The difference betweensome()&every()methods is thatsome()method stops checking as soon as the test condition is true. On the other hand,every()keeps checking until the last item in the array.
const arrayOfNames = [
"Chanakya",
"Maharana Pratap",
"Shershaah",
"Charak",
"Sangram",
];
const doesContainName = arrayOfNames.some((item) => item === "Shershaah");
console.log(doesContainName); // true
includes()
Theincludes()method checks if the array contains a particular value that is passed as an argument. It returns aboolvalue.
const arrayOfNames = [
"Chanakya",
"Maharana Pratap",
"Shershaah",
"Charak",
"Sangram",
];
const doesContainName = arrayOfNames.includes("Shershaah");
console.log(doesContainName); // true